Our world is on the brink of a technological revolution that will significantly change how we work, live, and interact with each other. By 2030, experts predict we’ll see an unprecedented array of devices in the workplace, including 8K virtual reality headsets, 3D printers, human-like AI, and a staggering 20 billion IoT devices. However, running these digital tools will require more bandwidth and power than ever. This is where Class 4 Power comes in. Recently developed by the National Electric Code (NEC), Class 4 Power is a solution designed to make power delivery safer, more accessible, travel greater lengths, and at much higher levels.
What is Class 4 Power?
Class 4 power is a cutting edge power delivery system that offers an impressive 450 volts of power, providing a substantial increase compared to traditional power delivery methods. This high-voltage power is delivered over a hybrid cable, extending the reach capability by a factor of eight. It’s important to note that this system does not carry data and focuses solely on delivering power more efficiently. In contrast with other power delivery systems like Power over Ethernet (PoE), Class 4 power stands out with its higher voltage and extended reach capabilities.
Class 4 power is in the early stages of development but will be a significant innovation in the built environment. Construction and IT workers will be much safer due to this new technology.
This system falls under the category of digital power. Unlike traditional analog power, which is delivered through a linear circuit, digital power uses a switching circuit to provide power more efficiently. Digital power behaves like a smart device in that it can self-adjust the voltage and current levels to suit the needs of whatever device it is powering. This capability directly translates to less energy being wasted and an overall increase in efficiency.
NOTE: Class 4 Power is not to be confused with Class 4 lasers or Type 4 Ethernet. Class 4 lasers are a classification system used to determine the safety of a laser device. They are considered the most potent and hazardous type of laser. Type 4 Ethernet refers to a specific classification of PoE that provides up to 90 watts of power to connected devices. Class 4 Power, on the other hand, is a high-voltage power delivery system.
What Are the 4 Classes of Power?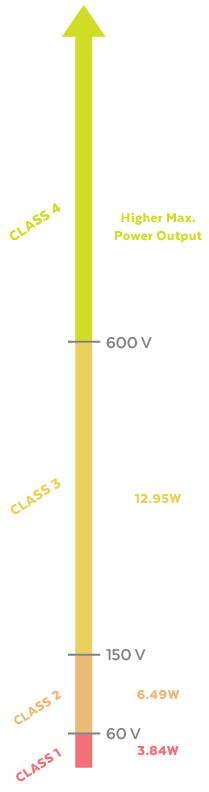
The term Class 4 comes from a classification system that designates the power capabilities of a device or component. These classes define the maximum power output. The higher the power class, the greater the power output. The four power designations are defined as follows:
- Class 1: Class 1 digital power operates at a voltage level typically below 60 volts. It is designed for low-power applications and utilizes basic circuitry to deliver a maximum power output of 3.84 watts.
- Class 2: Class 2 digital power operates at a voltage level between 60 volts and 150 volts. It employs more advanced circuitry to deliver a maximum power output of 6.49 watts. Class 2 power includes devices that require slightly higher power levels than Class 1, such as small sensors and low-power communication devices.
- Class 3: Class 3 digital power operates at a voltage level between 150 volts and 600 volts. It utilizes more complex circuitry to provide a maximum power output of 12.95 watts. Class 3 power is suitable for devices that require higher power levels, such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and high-resolution displays.
- Class 4: Class 4 digital power operates at a voltage level above 600 volts. It employs advanced circuitry to deliver a significantly higher maximum power output. Class 4 devices, such as high-performance industrial equipment, have much higher power requirements.
Each class builds upon the previous, with the higher classes capable of providing more power.
Fault-Managed Power Systems and Why They Are Better
Class 4 is fault managed. Fault-managed power systems (FMPS) are becoming increasingly popular in today’s digital age. In an FMPS, intelligent digital power technology detects and prevents faults before they can cause damage or downtime. These systems offer several advantages over traditional power systems, such as:
- Improved safety: FMPS systems can detect and prevent overloading, short-circuiting, and other electrical faults that pose safety risks. This feature is especially vital in critical applications where safety is a top priority, such as medical equipment or data centers.
- Improved reliability: FMPS systems can detect and prevent faults before they cause downtime, ensuring that critical equipment and systems remain up and running. This feature can provide a significant benefit in industries where downtime can cause substantial financial losses or safety risks.
- Reduced energy waste and lower overall costs: FMPS systems can deliver power more efficiently, reducing energy waste and lowering energy bills. Digital power technologies like Class 4 can help achieve this by providing power more efficiently and reducing energy waste.
Class 4 Benefits
Class 4 power offers several benefits over traditional power systems. Some of these benefits include:
- Increased Power Efficiency: Class 4 uses digital power technologies to deliver power more efficiently. There is a reduction in wasted power, resulting in lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Improved Safety: It detects and prevents overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults that can pose significant safety risks.
- Higher Power Capacity: Class 4 can handle higher power loads than traditional power systems, making it ideal for complex devices and applications.
- Real-Time Monitoring: It can monitor power consumption and device performance. Better control and optimization of power usage reduces energy waste and improves performance.
- Reduced Downtime: Class 4 power can detect and prevent faults before they cause downtime, ensuring that critical equipment and systems remain up and running. This reduces the occurrence of costly downtime and lost productivity.
 Packetized Power Delivery
Packetized Power Delivery
Packetized power delivery is a critical component of Class 4 technology, which enables a more efficient and reliable power delivery system. The system transmits each power unit over a data cable in a steady stream of hundreds of packets per second, all while performing continuous fault monitoring. This process allows for quick detection and response to any potential issues. If there is a fault, the transmitter immediately halts transmission to prevent risks such as severe shocks or device damage.
Furthermore, packetized energy transfer enables greater precision in energy management, allowing for more efficient and reliable power delivery to connected devices. By breaking down power delivery into discrete packets, Class 4 power delivery systems can adjust power delivery on a per-packet basis, allowing for greater control over power consumption and a reduction in energy waste. This packet-based approach also makes fault management more practical, allowing for rapid identification and correction of any issues.
Digital Electricity
Class 4 power delivery is made even more efficient and versatile with Digital Electricity™ technology. The system can accommodate both AC and DC loads by converting power into a DC stream during packet transmission. After being transmitted in packets, the energy is converted to match the needs of the output destination on the receiving end. The network allows for remote supervision and regulation of the power system, simplifying administration and monitoring procedures.
Cabling Needed for Class 4
To support this system, a hybridized solution of copper and fiber cabling is required. Belden DE Cables are the industry’s first-ever Class 4 cabling system that has received the UL 1400-2 certification. More manufacturers are sure to follow. These cables can carry electricity over distances of up to 800 meters. This is far beyond the limitations of Power over Ethernet (PoE), a mere 100 meters. Using fiber in the cabling system ensures minimal power loss over a longer distance.
Requirements for Class 4
It requires specialized equipment that can meet the safety and performance requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC). This includes fault-managed power systems, which continuously monitor for faults and shut down power delivery if any issues arise. Using these fault-managed power systems ensures that Class 4 Power is safe and reliable for various applications.
Class 4 Does Not Deliver Data
It’s important to note that Class 4 Power does not deliver data, meaning it’s only used for powering devices. These devices will still need a way to receive data. Happily, there is no conflict between the Class 4 Power technology and Power over Ethernet (PoE). IT administrators can implement PoE close to the end user and utilize Class 4 technology to simplify power and data delivery.
Class 4 Power is Empowering the Future of Advanced Technology
The rise of advanced technology in the workplace requires a robust and reliable power delivery system to meet the increasing demands of these digital tools. Class 4 Power, with its ability to deliver high power levels over longer distances, provides a promising solution to this challenge. The fault-managed design ensures a safe and efficient power delivery system, reducing the risk of electrical hazards. While Class 4 Power does not deliver data, it can work with other technologies like PoE to enable smart device capabilities. The availability of Class 4 cabling systems from industry leaders like Belden DE Cables is a testament to the potential of this technology. As the industry moves towards the digital age, Class 4 Power is set to play an essential role in powering the next generation of technology.

