No products in the cart.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a game-changer in modern networking, enabling power and data delivery to various devices over a single Ethernet cable. As businesses increasingly adopt hybrid networking configurations, understanding PoE device compatibility and interoperability is paramount.
While compatibility and interoperability are related concepts, they refer to different aspects of Power over Ethernet implementation. Let’s break down the distinctions between them.
What Is Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
Before unraveling compatibility and interoperability complexities, let’s quickly define PoE. Power over Ethernet is a technology that allows electrical power and data to be transmitted over a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installation and remote access for devices:
- Simplified Installations: PoE eliminates the necessity for separate power cables, reducing installation complexities and costs.
- Flexibility and Mobility: PoE facilitates the deployment of devices in locations without easy access to power outlets, offering greater flexibility and mobility.
- Remote Power Management: Centralized power delivery control allows for remote monitoring and management of connected devices, enhancing overall network efficiency.
The ability to centrally control and monitor power usage further allows organizations to optimize energy efficiency across their networked devices, contributing to a greener and more economical operational footprint. As PoE technology advances, its role in promoting environmentally friendly and cost-effective network solutions becomes increasingly significant.
What is PoE Device Compatibility?
Compatibility determines whether a specific device is designed to work with PoE and can receive power and data over a single Ethernet cable. This feature is especially beneficial when deploying a separate power source is impractical or inconvenient.
To comprehend device compatibility in PoE networks, let’s first grasp the functions of key components:
- PoE Injector: Powers a PoE device connected to a non-PoE switch.
- PoE Splitter: Separates power and data, supplying power to a non-PoE device.
- PoE Extender: Expands the power delivery span to include remotely installed devices.
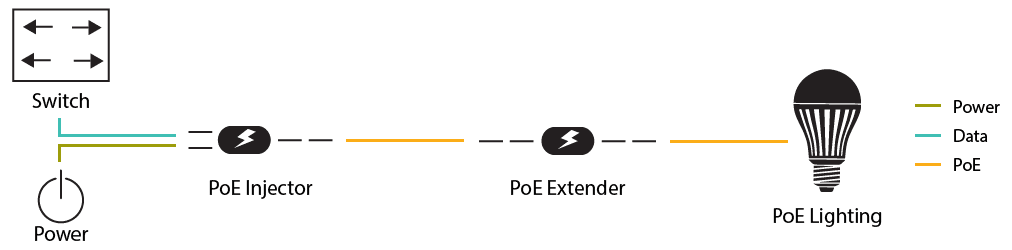

Together, these devices form the backbone of PoE networks, providing the flexibility and efficiency required for today’s dynamic and interconnected environments. Understanding the unique functions of each component is fundamental to optimizing PoE networks for varied applications in commercial offices, public buildings, transportation hubs, and academic institutions.
Criteria for Device Compatibility
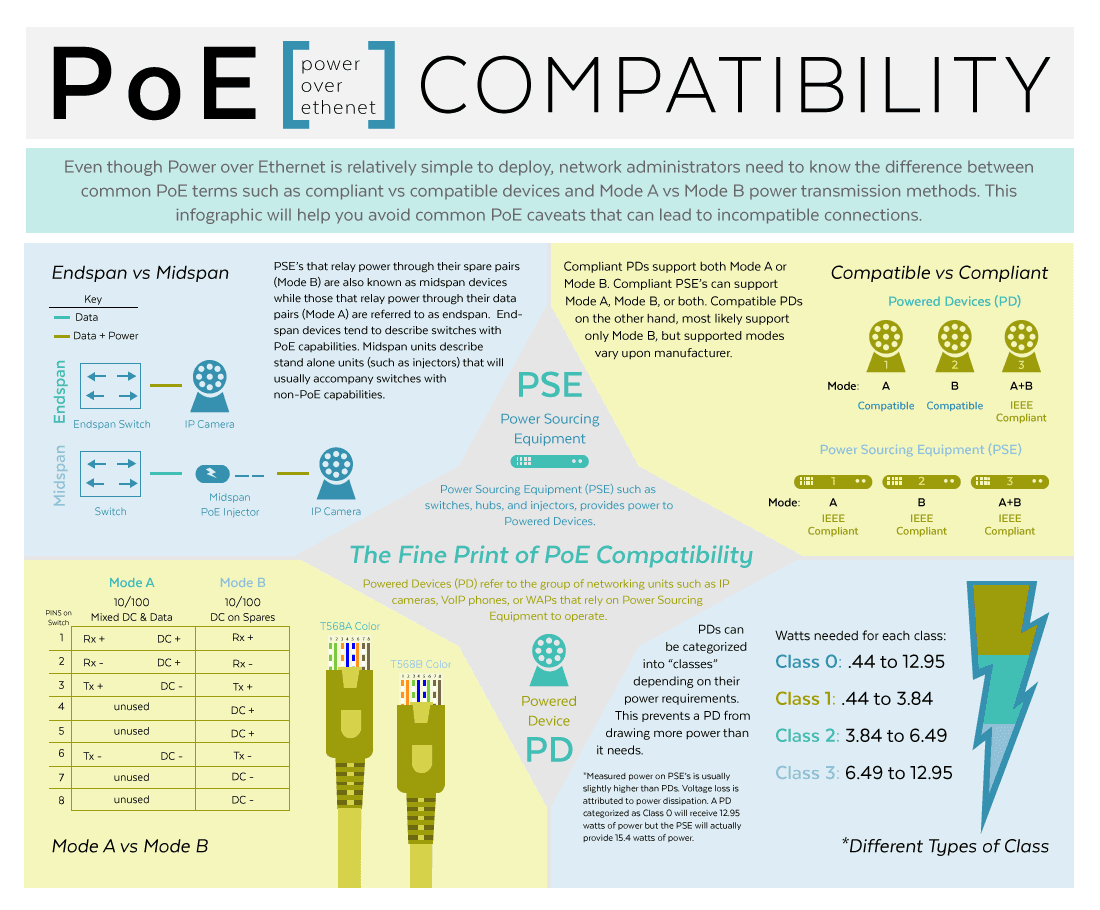
PoE-compatible devices adhere to established standards, such as IEEE 802.3af (PoE) or 802.3at (PoE+), ensuring uniformity in power delivery. These standards dictate the voltage, power, and communication protocols required to operate PoE-enabled devices successfully. For example, a PoE-compatible security camera can receive sufficient power via an Ethernet cable connected to a PoE switch/injector.
Assessing a device’s compatibility involves considering various criteria:
- PoE Standard Support: Verify the device complies with relevant standards (e.g., IEEE 802.3af, 802.3at, or 802.3bt).
- Power Requirements: Understand the device’s power consumption specifications and ensure your available power budget can meet these requirements.
- PoE Class: Confirm that the device falls within the appropriate PoE class.
- Voltage Compatibility: Align the device voltage requirements with the voltage provided by the PoE switch or injector.
- Pin Configuration: Verify the correct pin configuration for power delivery.
- Gigabit Ethernet Support: Ensure compatibility with Gigabit Ethernet if higher data transfer rates are needed.
- Auto-Negotiation: Confirm the device supports auto-negotiation for both data and power.
- Device Classifications: Understand PD (Powered Device) and PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) roles.
- PD Signature: Check that the device can adequately negotiate power requirements.
- Temperature and Environmental Considerations: Ensure the device is compatible with the environmental conditions present in the deployment area.
 Regularly consulting documentation, vendor guidelines, and PoE standards empowers IT professionals to make informed decisions about device compatibility in PoE networks. Testing devices before deployment in a controlled environment can help identify and address compatibility issues.
Regularly consulting documentation, vendor guidelines, and PoE standards empowers IT professionals to make informed decisions about device compatibility in PoE networks. Testing devices before deployment in a controlled environment can help identify and address compatibility issues.
Importance of Compatibility
PoE compatibility is crucial for simplifying installations, reducing cable clutter, and enabling devices to function efficiently where access to conventional power sources may be challenging. It ensures that devices can seamlessly integrate into PoE networks and receive power without additional infrastructure.
What Is Interoperability?
The broadest definition of interoperability is the ability of systems, applications, devices, and services to work seamlessly together. In the context of PoE devices, interoperability ensures that different devices, often from different manufacturers, can communicate with each other effectively, contributing to the network’s overall efficiency.
Notably, PoE device manufacturers often host events like “plugfests” to enhance interoperability, fostering collaboration and interoperability among devices from various manufacturers. Such events help ensure that devices with varying specifications and standards can coexist, communicate, and share power without compatibility issues.
Criteria for Interoperability:
Evaluating the interoperability of devices within a system requires more than just looking at voltage levels and power classes. This process involves implementing standardized communication protocols and negotiation processes, allowing devices to understand and interact with each other on the network. For instance, a PoE switch with exceptional interoperability can power and communicate seamlessly with PoE-compatible devices from multiple manufacturers.
Importance of Interoperability:
Interoperability is crucial for the scalability and flexibility of PoE networks. It enables users to mix and match devices from different vendors and promotes competition and innovation. Without interoperability, communication issues or power delivery inconsistencies arise, potentially hindering the seamless integration of PoE devices from various sources.
The Importance of Distinction
Understanding compatibility and interoperability is not just a technicality but a strategic advantage. While compatibility ensures devices work within the PoE ecosystem, interoperability guarantees seamless communication between devices. Evaluating both aspects of inter-device communication is fundamental for optimizing network performance and providing a future-ready infrastructure.
In a rapidly advancing technological landscape, embracing these considerations and best practices will empower IT professionals and businesses to harness the full potential of Power over Ethernet, making informed decisions that align with current standards and future developments. Stay vigilant, stay connected, and you’ll ensure your PoE network remains robust.
Explore PoE Solutions
Ready to optimize your Power over Ethernet experience? Explore Versa Technology’s cutting-edge solutions designed for seamless compatibility and durable interoperability. From PoE switches to advanced devices, our technology ensures your network will thrive in today’s ever-evolving landscape.

