PoE Solutions in Automation
In the wake of shrinking labor pools and accelerating technology advancements, industries need to find more cost-effective ways of meeting customer demands. Automation offers a path forward. Machine-based efficiency is a flexible method of streamlining processes and maximizing production levels. Power over Ethernet (PoE) has taken automation to the next level by connecting various industrial systems in a more centralized business model. PoE solutions in automation not only provide a more affordable way to add infrastructure but also simplify installations, reducing complexity and expanding potential installer options.

What Is Automation?
Automation refers to using various technologies to minimize human input in processes. Today, industries are making automation the primary focus of their material handling, production, and quality control improvement efforts.
The following are some of the critical benefits of industrial automation:
- High Production Rates: Automation systems such as robotics help industries perform repetitive and tedious tasks for long hours without fatigue or mistakes. Reducing the human input needed in these processes reduces downtime and increases production rates.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation helps to cut down operational costs in several ways. By performing a lot of work with minimal human interaction, industries can reduce labor expenses, and the increased accuracy associated with automation minimizes material wastage. Additionally, sensors, actuators, and other information networks help to gather data on equipment and operational patterns. This information is critical for the continuing development of cost-efficient operations.
- Improved Safety: Maintaining safe operations is critical for industries as it helps avoid injuries, damages, and legal problems. Automated systems have taken over dangerous industrial operations, especially the ones that would have required employees to work in close physical proximity to machinery. The ability to operate machines from a distance helps to minimize the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Better Product Quality: Automation produces consistent results while monitoring and rectifying any faults in the systems to help achieve the highest product quality.

What Is PoE?
Power-over-Ethernet is a technology that transmits power and data through Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6A Ethernet cables to industrial machine components. Adding PoE capability to Ethernet cables eliminates the need for separate wiring.
How Does PoE Work?
The PoE system begins with Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE), a switch, or an injector that provides power to the connected powered devices (PD). PDs include IP cameras, VoIP phones, access points, and more. The PSE sends direct current (DC) voltage over the Ethernet cable. Voltage levels depend on the PoE standard and the device’s power requirements. PoE systems use isolation mechanisms to separate power and data circuits, ensuring safety and preventing electrical interference.
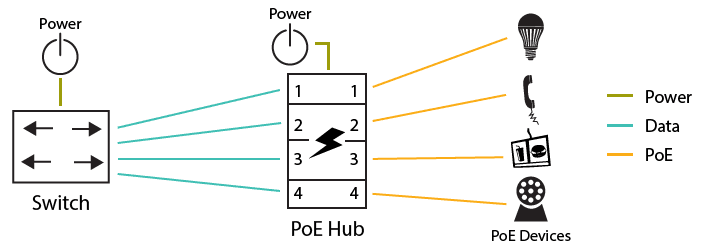
What are the Advantages of PoE?
Let’s look at some of the key advantages of using PoE technology:
Low installation Costs
Since PoE delivers power and data over standard Ethernet cables, there is no need for DC/AC outlets and individual device power supplies. This added efficiency eliminates the need for buying extra PD equipment and hiring an electrician to install additional power outlets. Moreover, Ethernet cables are often pre-installed in commercial buildings.
Ease of Operation and Flexibility
PoE allows businesses to scale up networks without requiring significant infrastructural changes. Flexible installation of devices throughout a workspace is possible with Ethernet connections, eliminating the need for proximity to power outlets. Ethernet signals can travel up to 100 meters (329 feet) before requiring a signal boost. By inserting a PoE extender, that range can extend up to 1000 meters, depending on the power requirements of a specific device. Extenders are available for single-use and industrial-grade applications, making them both affordable and durable.
Remote Management
It’s easy to manage and configure PoE devices remotely. An IT administrator can adjust settings, update firmware, or troubleshoot devices without requiring physical access. By enhancing overall network management efficiency, PoE is particularly advantageous when devices are located across multiple sites.
Reliability and Backup Power
In industrial spaces where reliability is critical, PoE combines with backup power solutions like Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) to ensure the continuous operation of essential networks. That means vital security cameras or network switches can continue to function during power outages.

What is PoE in Automation?
Industries use PoE to provide power and data to the various machine components that facilitate automation. Regarding industrial automation, PoE connectivity systems are classified according to their IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standard, which states the maximum power per switch a system can handle.
The three main classifications of PoE systems include:
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3af is commonly known as the Standard PoE and operates within a voltage range of 44-57V, delivering up to 15.4 watts of power per port. The low power output makes IEEE 802.3af suitable for devices with low power demands, such as those used for IP phones, basic surveillance cameras, and access control systems.
IEEE 802.3at (PoE+)
IEEE 802.3at is an updated version of IEEE 802.3af and operates within a voltage range of 50V to 57V and a supply current of 10-600mA. It delivers a maximum of 30 watts per PSE port and ensures each port operates at a minimum output of 25 watts. PoE+ is a step up for devices that need more power than IEEE802.3af, and its applications include wireless access points, advanced IP cameras, and video conferencing equipment.
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++)
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) is the most recent PoE system and the highest power standard, delivering up to 60 or 100 watts. PoE++ is categorized into Type 3 and Type 4 and increases power delivery through multiple pairs of Ethernet cables. The PSEs under IEEE 802.3bt identify and allocate power based on the maximum power requirement of the device. PoE++ is primarily used for industrial automation systems that require a substantial amount of power to operate, such as pan-tilt-zoom cameras, high-performance wireless access points, and LED lighting systems. It’s important to note that both type 3 and type 4 mods type 3 and type 4 models are backward compatible with IEEE 802.3at and IEEE 802.3af PoE systems.

What are PoE Solutions in Automation?
Here’s an overview of network components commonly found in Power over Ethernet (PoE) installations:
- PoE Switches: PoE switches are network switches that deliver data and electrical power to PoE-enabled devices in industrial settings.
- PoE Injectors: PoE injectors are usually inserted between the regular network switch and the PoE device, allowing for power and data transmission over the same Ethernet cable.
- PoE Splitters: PoE splitters separate power and data from an Ethernet cable. They are used when a PoE-enabled device requires power and data, but the network switch or injector doesn’t support PoE. The splitter extracts the power and supplies it to the device while sending the data to the connected non-PoE switch or device.
PoE Extenders: PoE extenders receive PoE power and data from the source and then retransmit it to the remote device to extend the network range.

What are Factors to Consider When Choosing PoE Solutions?
When choosing PoE solutions for your industrial automation process, here are the key factors to look out for:
Power Requirements
PoE solutions should be able to transmit enough power to support all the automated processes in an industrial setting. Before selecting a PoE device, analyze the scope of the automated processes it will be used for and get an accurate measure of the power requirements to ensure proper functioning. For example, large-scale operations with power-hungry devices like PTZ cameras or industrial robots may want to consider IEEE 802.3bt. Type 4 PoE devices can deliver power up to 100 watts, enabling the maintenance of continuous and efficient operations.
Network Speed and Scalability
PoE solutions should provide high-speed data transfer to support real-time data transmission, which is crucial for monitoring and controlling processes. Higher speeds reduce latency and enable quick decision-making. The internet speed required for industrial operations depends on how fast data needs to be processed from one function to another. For example, Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) is ideal for data exchange between cameras, sensors, and control systems. Additionally, PoE solutions should accommodate expansion and additional devices without disrupting operations.
Manageability
Manageability is a measure of how easy it is to configure, monitor, and maintain PoE networks in industrial automation. To enhance manageability, choose PoE systems that provide comprehensive management tools such as SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration, and Access Control Lists (ACLs). This combination of tools ensures easy control and continuous operation of the automated systems.
Security
PoE solutions should include built-in security features like Virtual LANs (VLANs), access controls, and encryption to protect sensitive data. Enhanced network protection reduces the risk of cyberattacks and protects the integrity of the industrial automation process.

Applications of PoE Solutions in Industrial Automation
PoE Solutions are widely used in Industrial Automation for various applications. Here are some common applications:
Robotics
Major companies across the world use pre-programmed robots to perform repetitive tasks on their manufacturing floors. This type of automation helps to ensure quality and prevent mistakes even during long hours of continuous operations. By providing power and data through a single cable, PoE simplifies the integration of robots in industrial systems, especially those requiring constant data feedback, e.g., stocking, packaging labeling, and assembly.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators are industrial automation equipment types that help collect real-time information on issues such as pressure, speed, and vibrations in various manufacturing processes. PoE-based sensors and actuators play a crucial role in industrial automation due to Ethernet’s ability to provide stable connections.
Communication Networks
PoE-based communication network systems such as industrial IoT devices and wireless access points provide reliable data transmission, enabling easy control, monitoring, and coordination of industrial processes. The networks connect various devices, such as PLCs, sensors, and actuators, creating seamless communication. PoE network systems facilitate easy integration with enterprise systems, allowing data analytics and remote management.
Control Systems
Industrial automation relies on control systems such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and distributed control systems (DCS) for centralized control of machinery and processes. These systems help execute tasks based on predefined logic. PoE provides data to connected devices, simplifying cabling and reducing installation costs, making it an efficient solution for industrial control systems.
Cyber Security
Through features offered in managed switches, PoE systems enhance cybersecurity in industrial automation by isolating critical networks and reducing the likelihood of attacks. For example, PoE-powered cameras and sensors in a manufacturing facility can be separated from the main control network. PoE-based devices also integrate with access control systems such as card readers to prevent unauthorized access and tampering with automation systems. These devices also receive information and firmware updates remotely, minimizing human interaction with automation systems.
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems
As with sensors, automation through SCADA systems is essential for monitoring equipment performance and efficiency. SCADA systems have software and hardware components such as actuators, field controllers, supervisory computers, HMI software, and communication infrastructure. PoE enhances the efficiency of SCADA systems by extending its reach to sensors on production lines. This enhancement allows for precise monitoring and efficient adjustments.
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication
Industrial automation relies on Machine-to-Machine communication (M2M) to transmit data between electronic and mechanical devices. PoE allows devices to receive power and data through a single cable, simplifying connectivity and eliminating the need for human interaction. This simplification allows M2M devices to operate efficiently and ensures seamless data exchange and communication in industrial automation processes.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IIoT is the connection of various industrial equipment, machines, sensors, and other devices to the Internet and collecting data from them to improve operational efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. PoE systems can provide enough power and data to connect all the industrial equipment in a facility under one system. For instance, the IEEE 802.3bt type carries the highest data rates of Gigabit Ethernet and beyond while still delivering high power voltage, making it easy to achieve IIoT in large-scale operations.

Frequently Asked Questions about PoE Solutions in Automation
What is Power over Ethernet (PoE) Technology?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows transmission of power and data over one Ethernet cable, eliminating the complexity and costs associated with installing separate cables.
How does PoE work?
PoE uses a switch or Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) to simultaneously transmit and provide power and data over Ethernet cables to Powered Devices (PDs), such as IP cameras, phones, and access points.
What are the different PoE standards?
There are four primary PoE standards: IEEE 802.3af (PoE), IEEE 802.3at (PoE+), and both IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) and IEEE 802.3bt (Hi-PoE). Each option delivers different power voltage levels.
Which devices can be powered using PoE?
PoE can power a wide range of industrial automation devices, including IP cameras, VoIP phones, access points, sensors, industrial robots, communication networks, SCADA systems, and more in industrial automation.

Versa's PoE Solutions in Industrial Automation
PoE offers numerous advantages for industrial automation operations. These advantages include low installation costs, ease of operation and flexibility, remote management capabilities, reliability with backup power, and enhanced network security. Choosing the right PoE solution to meet specific power requirements and network speed in industrial automation processes is now easier with the availability of different standards.
Versa Technology offers the best PoE solutions for various industrial automation needs, from robotics to cyber security maintenance. Contact us today to request a quote.

- PoE Solutions in Automation
- What Is Automation?
- What Is PoE?
- What are the Advantages of PoE?
- What is PoE in Automation?
- What are PoE Solutions in Automation?
- What are Factors to Consider When Choosing PoE Solutions?
- Applications of PoE Solutions in Industrial Automation
- Frequently Asked Questions about PoE Solutions in Automation
- Versa’s PoE Solutions in Industrial Automation
