As city populations increase every year, they get crowded, and resources are stretched to their limits. Today’s cities must evolve to meet the needs of their residents. Here are some interesting statistics:
- In 2020, 56 percent of the global population lived in cities.¹
- In the same year, 83.6 percent of North American countries’ populations lived in cities.¹
- The United Nations predicts that 68 percent of the world’s population will live in urban areas by 2050.²
Cities must deal with the often overwhelming problems of social and economic imbalance among their citizens. One of the most viable ways to increase a city’s effectiveness and efficiency is through technology.
What is a smart city?
Let’s start with the digi.city definition:
Smart Cities use connected technology and data to (1) improve the efficiency of city service delivery, (2) enhance quality of life for all, (3) increase equity and prosperity for residents and businesses.³
City management is complex. The goal needs to be the improvement of the quality of life for its citizens. Each individual must be offered adequate resources to be self-sufficient in their environment in a way that consumes the least amount of resources. This is a tall order.
A smart city uses Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) to create, install, and promote practices that address these urban challenges. Citizens are encouraged to engage with smart city ecosystems that improve things like energy distribution, trash collection, traffic congestion, and even air quality using the Internet of Things (IoT). Here are some examples:
- Connected traffic lights: Sensors send data to the traffic lights that inform them of real-time traffic conditions.
- Connected cars: Communication with parking meters and electrical vehicle (EV) charging docks that advise drivers on available spots.
- Smart garbage cans: Can automatically send data to waste management companies to pick-up refuse as needed.
- Smartphones: Can become a mobile driver’s license or ID card (digital credentials) to simplify city/government services access.
What are the benefits of a smart city?
There are many benefits when cities use smart technology, and many are vigorously engaging in these upgrades as we speak. According to Statista, technology spending on smart city initiatives worldwide will increase from 81 billion U.S. dollars in 2018 to 189.5 billion in 2023.⁴
Following are ten of the most significant benefits of the use of smart technology by cities:
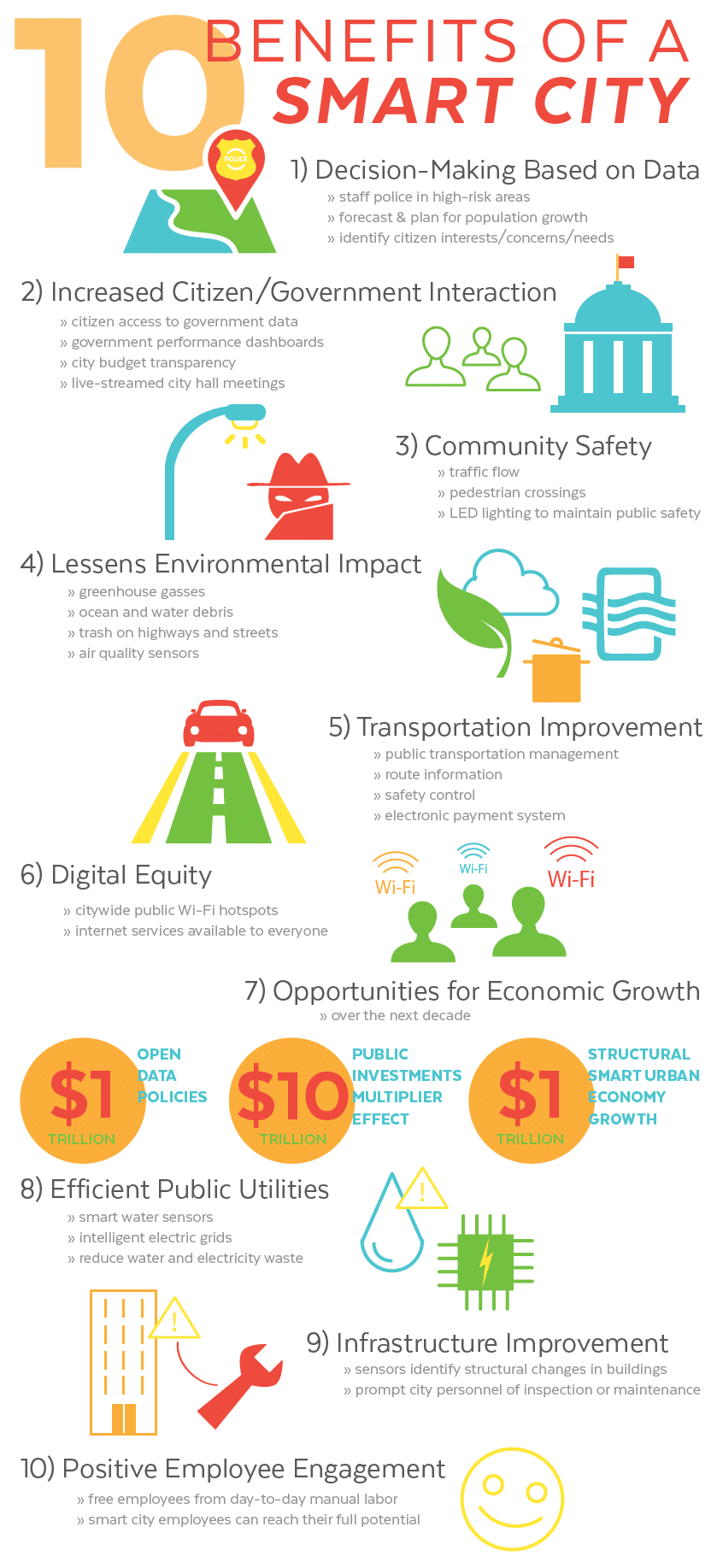 1) Decision-Making Based on Data
1) Decision-Making Based on Data
Big data and connected devices enable cities to access more information than ever before. With this plethora of data, city planners can glean invaluable, real-time metrics that give them insights to make the best decisions possible.
This type of technology provides data to help identify and staff police in high-risk areas, forecast and plan for population growth and citywide expansion, identify citizen interests, concerns, needs, etc.
2) Increased Citizen/Government Interaction
Things like collaboration tools, intuitive websites, mobile apps, self-service portals, and online accounts enable residents to engage with their city government and its services in a quick, user-friendly way.
The ability for citizen access to government data, interactive maps, government performance dashboards, city budget transparency, live-streamed city hall meetings, and a healthy city media presence all make a city attractive to live in and help its citizens to trust city officials.
3) Community Safety
Simply put: A smart city is a safer place to live. Technology such as plate recognition, gunshot detectors, connected crime centers, next-generation 911, and police body cameras give law enforcement an advantage.
Here is another example: In 2016, the city of San Diego invested in smart streetlight technology. In addition to informing the town of things like traffic flow and pedestrian crossings, they found that the LED lighting helped them maintain public safety. According to LT. Jeffrey Jordan, Chief’s Office/Special Projects of the San Diego Police Department:
We use technology as a means of enhancing investigations, preventing crime, and interacting with community members to ensure their safety. We have only 1800 officers for a city of 1.3 million people spread out over 300 square miles. We can’t be everywhere all the time. But we can use the data being collected by smart streetlights to help provide evidence for violent crime investigations and fatal or near-fatal car collisions.⁵
4) Lessens Environmental Impact
Cities need to deal with environmental issues such as greenhouse gasses, ocean and water debris, and trash on highways and streets. Smart cities encourage the construction of energy-efficient buildings, the employment of air quality sensors and renewable energy sources to decrease their ecological footprint.
For instance, medical problems that stem from pollution kill millions of people every year. Deploying air quality sensors around a city can help track peak times of low air quality, identify the causes of pollution, and provide information to make sound action plans.
5) Transportation Improvement
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) have the potential to enhance travel through a city significantly. ITS includes:
- Public Transportation Management: Provides automation and planning that encourages travel throughout a city and offers quick responses to schedule deviations or emergencies, ensuring the safety of the travelers.
- Route Information: Provides easy route scheduling, real-time information about traffic conditions, travel time, alternative routes, toll fares, and parking availability.
- Safety Control: Provides assessment of driving capabilities, road conditions, and vehicle performance. Advanced sensors assist drivers during poor visibility due to weather conditions or night driving.
- Electronic Payment System: One single electronic payment can buy tickets for different transportation modes: buses, metros, trains, etc.
6) Digital Equity
To ensure each citizen has access to a smart city’s technology, they must take steps toward providing digital equity. Adopting citywide public Wi-Fi hotspots needs to be strategically placed throughout a city to ensure internet services are available to everyone. Cities such as Portland, OR, Philadelphia, Austin, TX, Chattanooga, and San Jose, CA have all adopted smart technologies with built-in digital equity considerations.
7) Opportunities for Economic Growth
According to a white paper authored by ABI Research:
The impact of smart city technologies on economic development and gross domestic product (GDP) growth, in particular, will materialize according to three dimensions or phases:
- Open Data Policies: Incremental GDP of close to US$1 trillion over the next decade
- Public Investments Multiplier Effect: Incremental GDP of US$10 trillion over the next decade
- Structural Smart Urban Economy Growth: Recurring, sustainable growth by 2.8% by 2026; (US$) 10 trillion GDP generated in the next 10 years.⁶
These statistics indicate that when cities innovate and engage in smart technologies, the result is significant GDP growth expansion. Large private enterprises are teaming up with city governments and investing millions of dollars in smart city infrastructure and initiatives—and intelligent cities attract new residents and businesses.
8) Efficient Public Utilities
Smart water sensors and intelligent electric grids reduce water and electricity waste, as well as damages. An example comes from Virginia Beach, which has deployed 40 smart water sensors that can predict floods from rain or storm surges for up to 36 hours in advance.
9) Infrastructure Improvement
Smart technology provides cities with analytics that predict and identify infrastructure areas that require repair or replacement before a complete failure occurs. Intelligent sensors send data that identifies structural changes in buildings and bridges and send messages that prompt city personnel of inspection or maintenance needs. This not only saves tax dollars but prevents injury or death.
10) Positive Employee Engagement
When cities use smart technologies such as those discussed above, they can free employees from many forms of day-to-day manual labor. With the ability to streamline these tedious processes, smart city employees can reach their full potential while providing excellent, upgraded services.
Wondering about how smart cities are powered? Check out this blog.
_______________________________________
1 World Economic Forum: How has the world’s urban population changed from 1950 to today?
2 United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs: 68% of the world’s population projected to live in urban areas by 2050, says UN
3 digi.city: Definitions: What is a smart city?
4 Statista: Technology spending on smart city initiatives worldwide from 2018 to 2023
5 Security Infowatch.com: Public Safety is at the Heart of the Smart City Movement
6 ABI Research: Role of Smart Cities for Economic Development

