Fast-growing companies and established organizations are moving their applications to the cloud, with over 28% of total IT budgets dedicated to cloud computing. In addition, 70% of organizations have at least one application running in the cloud. This means businesses are realizing the advantages of cloud computing and adopting it. However, experts believe that the cloud has reached its limit. Now, edge computing is taking over.
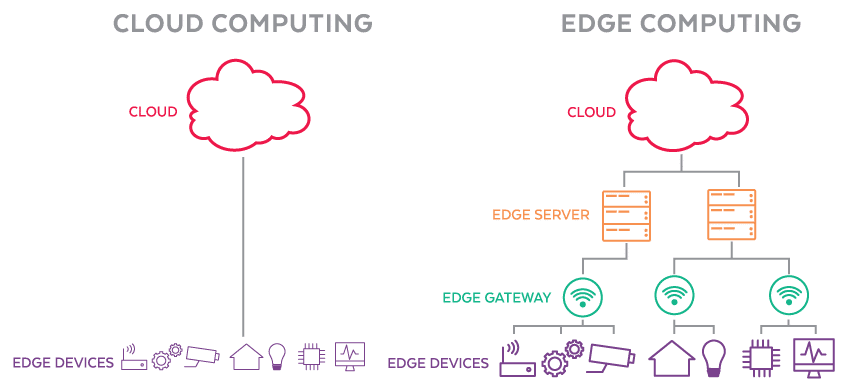
As a subsection of cloud computing, edge computing involves hosting applications closer to end users. This is done in small edge data centers or on customer premises. It differs from the the cloud system, where applications are hosted in a core data center. But what exactly is edge computing, and why do networks need it?
What is Edge Computing?
Edge is a distributed information technology (IT) architecture designed to process client data at the network’s periphery, closer to where the data originates. It is an emerging computing model involving different networks and devices at or near the user. As a result, businesses using edge computing can process data at incredible speeds and volumes, resulting in better real-time action-led outcomes.
With edge computing, companies can leverage unique advantages over traditional models where computing is centralized at a primary data center. Edge allows businesses to improve how they use and manage physical assets and develop new interactive human experiences. Here are the key components of edge computing:
- Edge devices: These include devices like smart speakers and phones that collect and process data locally while remaining connected to the physical world. Other sophisticated devices include the Internet of Things (IoT), robots, vehicles, and point of sale (POS) systems.
- Network edge: Edge computing requires extremely powerful wireless connectivity with low latency and high cellular speed, like 5G. This allows for exciting edge computing opportunities, such as autonomous drones, innovative city projects, and remote telesurgery.
- On-premises infrastructure: These include components, such as servers, containers, bridges, and routers, used for managing local systems and linking to the network.
 Why Networks Need Edge
Why Networks Need Edge
Hospitals, retail stores, and factories are already using edge to process the most sensitive data and power crucial systems that must operate safely and reliably. Here are some reasons why networks need edge computing: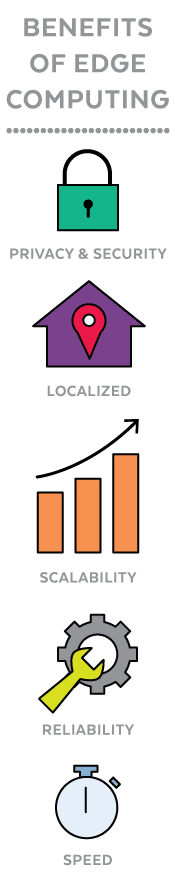
Heightened Privacy and Security
With increasing concern over adding thousands of internet-connected devices and sensors to a network, edge computing allows enterprises to process data locally and store it offline. This reduces data transmission across the network, helping businesses to be less vulnerable to security threats. It also decreases the transmission of sensitive information to the cloud, enhancing privacy within the organization.
Localized
Edge computing reduces the amount of data transfers sent between devices and a centralized cloud. With less data in cloud storage, enterprises can process most of their data on-premises or in small edge data centers near the company. It is an effective way to remain local while embracing cloud computing.
Scalability
Although expanding or modifying dedicated data centers can be costly, edge computing allows enterprises to deploy devices with their processes and data management tools in a single phase. In addition, this sophisticated scheduling technique increases the effective utilization of edge resources, scaling the edge server by allocating minimum edge resources to a specific offloaded task. The advantage of scalability plays a critical role for enterprises looking to scale up or down seamlessly and more efficiently.
Reliability
Edge computing allows enterprises to collect and process data with little or no hindrances, including when there is a poor internet connection. In addition, enterprises can continue their operations if one or more edge devices fail, as it does not alter other edge devices within the system. This facilitates the reliability of connected systems, reducing downtime and other issues associated with using the centralized cloud. For example, an edge computing device like a voice assistant may continue to offer service to local users even when cloud service or internet service fails.
Speed
Without centralized cloud and data center locations, companies can process data more quickly and reliably. Diminished data quality, network bottlenecks, and data latency are some challenges associated with sending data to a central office all at once. Edge computing incorporates analytical computational resources at or near the data source, increasing the responsiveness and throughput of applications. It can also mimic human perception speed, which is essential for critical applications like augmented reality.
More Efficient Operations
Edge computing enables enterprises to optimize their everyday operations by rapidly processing enormous volumes of data at greater speeds at or near where data is generated. This process is much more efficient than sending all collected information to a centralized cloud or a primary data center several miles away. Therefore, edge eliminates excessive network delays and performance issues associated with the centralized cloud.
Applications for Edge Computing
Edge application services decrease the volumes of data being moved, the resultant traffic, and the distance that data must travel, resulting in lower latency and transmission costs. Research on computation offloading for real-time applications, like facial recognition algorithms, proved effective in response times.
In another research study conducted on resource-rich machines, the data source also showed performance improvements when some tasks were unloaded to the edge node. Contrarily, offloading each task may lead to a slowdown because of transfer times between nodes and devices. Hence, defining an optimal configuration based on the workload is crucial.
Edge also makes energy management more efficient through IoT-based power grid systems that allow communication of electricity and data for monitoring and operating the power grid. Cloud gaming is another edge application where selected aspects of a game can run in the cloud. The rendered video can reach lightweight clients operating devices like VR glasses and mobile phones.
In Summary
Versa Technology, Inc. is a leading U.S.-based provider of last-mile IT networking technology. It’s also the largest supplier of Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch technology products. Follow us on Twitter.