Cable companies have arrived at a tipping point— their customer base consists of a growing number of broadband subscribers and a declining amount of cable subscribers. Customers are cutting the cord on cable and relying on online streaming and OTT (over-the-top) content to watch their favorite videos.
Broadband providers have been relying on Docsis to adjust for these changing consumer trends. Now that cable TV is no longer cable companies’ primary product offer, DOCSIS 3.0 will be helping cable operators upgrade their broadband services.
Docsis 3.0 features downstream rates of 42.88 Mbps and will allow cable operators to provide faster broadband speeds to their customers via their existing hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) networks.
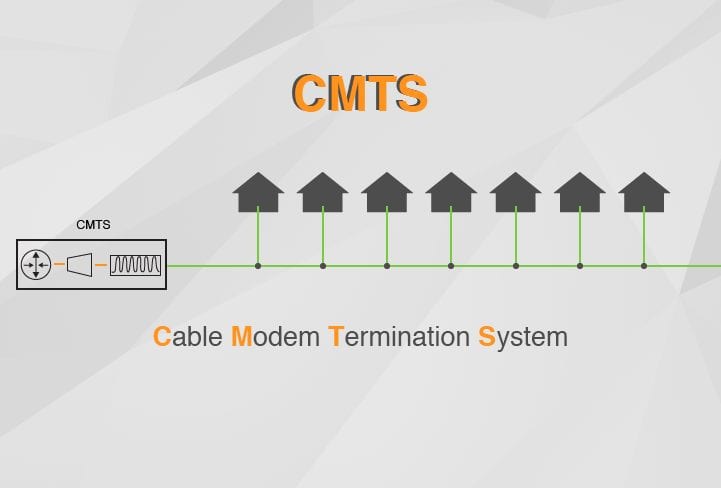
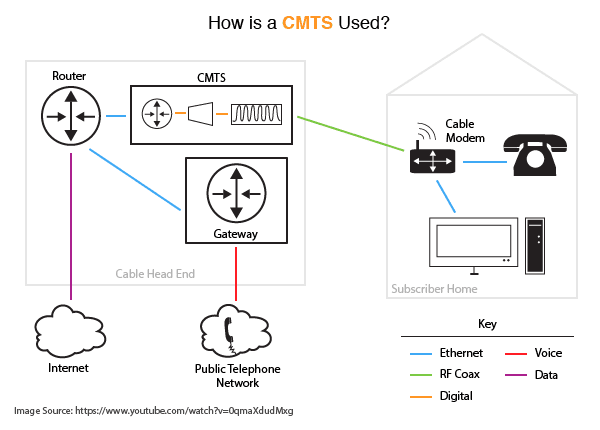
DOCSIS 3.0 Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTSs) come in two forms: Integrated and Modular. Both CMTS provide efficient services to different-sized networks.
Integrated vs. CMTSs
Integrated CMTSs (I-CMTS) typically comprise of a router, a filter (to throttle bandwidth) and a high frequency radio front (RF) end that modulates and demodulates incoming and outgoing data. These components have a fixed functionality in an I-CMTS architecture.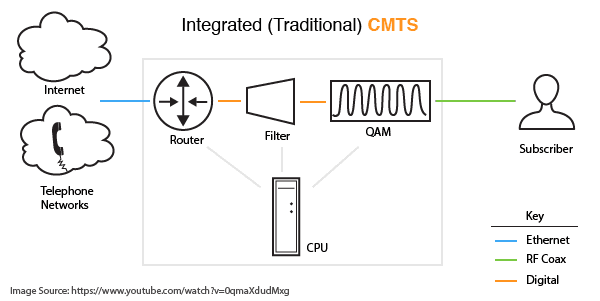
Modular CMTS (M-CMTS) on the other hand, house these components (router, filter, and RF front end) in separate shells. This gives MSO’s a dynamic approach to networking. MSO’s can assign different component ratios according to the distinct requirements of an application.
For example, to support an application that requires more RF capabilities, MSO’s can amplify RF support and reduce routing power.
These chassis are designed to support thousands of subscribers and cost approximately $30,000. They are ideal for large-scale deployments where economies of scale give networks the opportunity of receiving a larger ROI.
Small Scale HFC Deployments
These chassis however, are inefficient for smaller scale deployments that comprise of a few hundred subscribers.
I-CMTSs are more fitted to meet the demands of small scale deployments.
Mini-CMTSs in particular, typically cost between $8,000-10,000 and can support up to 500 subscribers per CMTS. These units are ideal for multidwelling units (MDU) such as condominiums, apartments, hotels, and small communities.
Channel Bonding and Dynamic Frequency Allocation
Both Modular and Integrated CMTs can take advantage of DOCSIS 3.0’s channel bonding and dynamic frequency allocation features—two powerful new improvements that work in conjunction with each other and accelerate throughput.
Channel bonding essentially bonds several frequencies together to create a larger pipe to increase throughput. According to the VoIpe Firm, channel bonding yields “subscriber data speeds of up to 160 Mbps”.
With dynamic frequency allocation, MSOs can use channel bonding to temporarily increase the bandwidth of certain subscribers that require more bandwidth. Previous DOCSIS standards offer fixed bandwidth to each subscriber.
Even though cable subscribers are plummeting, cable operators can entice their customer base with faster broadband speeds. Both Integrated and Modulated CMTSs can take advantage of the speed boost that DOCSIS 3.0 offers.
Docsis 3.0 can help cable operators fortify their broadband infrastructures to support the growing demand for high-speed broadband (IPTV, Over the top content)