There is a relatively new Power over Ethernet (PoE) standard, and it has several names: IEEE 802.3bt, 4 Pair PoE, PPOE, UPOE, PoE++. (For this article, we will refer to this technology as PoE++.) This newest standard was ratified by the Institute of Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in September 2018 and has enabled organizations to save money and labor while making installations safer.
PoE Before 802.3bt
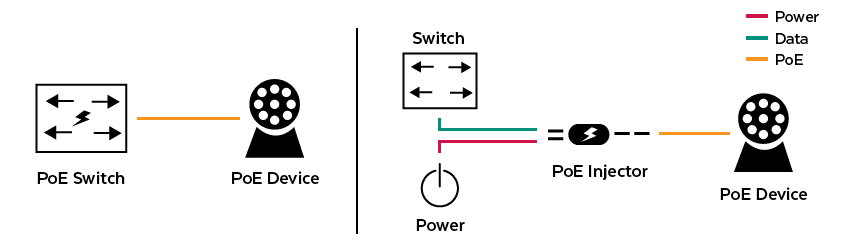
Although PoE has been around for almost two decades, it can still be confusing and misunderstood. PoE is a technology that enables network cables to carry electrical power. For example, a standard digital security camera requires two connections: a network connection to communicate and a power connection to deliver electrical power to the device. However, if the security camera is PoE-enabled, it will only need the network connection, as the network cable will also deliver electrical power.
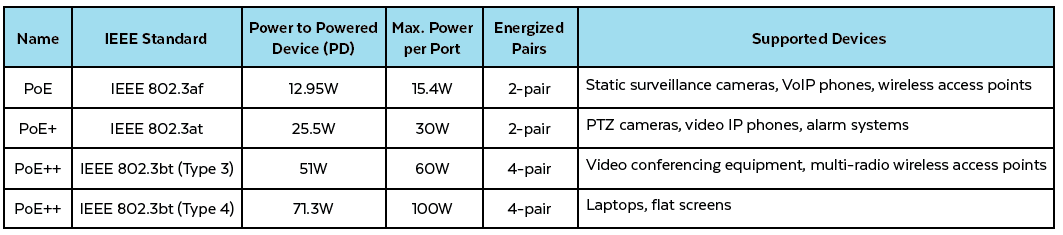
PoE 802.3af (also known as PoE or PoE Type I) was ratified in 2003 and supports a maximum power consumption of 15.4W. PoE 802.3at (also known as PoE+ or PoE Type 2) was approved in 2009 and delivers power up to 30W. These two PoE standards are compatible with devices such as IP phones, simple IP cameras, and indoor wireless access points. However, with new applications such as LED lighting, smart buildings, and the internet of things (IoT), there was a need for higher bandwidth and power supply.
Before the ratification of PoE++ (802.3bt), there were non-standardized methods to figure out this need for more power. According to SecurityInfoWatch, the leading trade association for global security providers:
In these scenarios, there were two options for manufacturers to engineer products:
- Option 1 – Use both PoE and a separate low voltage AC or DC power connection, i.e., PoE and 24VAC. This would enable the PoE to power the PTZ camera, while the 24VAC would power the heater/blower or the infrared LEDs.
- Use a non-standard PoE called “Hi-PoE” or “PoE++” that delivers up to 60W of power. Some would think that this is the same as 802.3bt Type 3; however, it is not.¹
It is important to note that neither of these options is compatible with standardized equipment.
The Latest Standard of PoE
IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) introduces two new Types of PoE:
- PoE Type 3 enables two or all four twisted pairs in a copper cable to supply a maximum power of 60W.
- PoE Type 4 enables all four twisted pairs in an Ethernet cable to supply a maximum power of 100W.
What IEEE 802.3bt Brings to the Table
PoE++ allows the transfer of as much as 71W to a powered device (PD) with a maximum cable length of 100m (328 ft.). This increased power is delivered across all four twisted pairs. PoE++ devices offer high power and high speed at the same time.
PoE++ devices currently run smart buildings, healthcare facilities, and smart offices. To a lesser extent, PoE++ is even being used in smart homes. However, this power technology is proliferating in a few “niche” areas.
Industrial Automation
Industrial automation is growing rapidly and is driving many changes in networking as a whole. Manufacturers are demanding more responsive systems that cut costs and help push efficiency to the max.
PoE++’s higher wattage is perfect for massive sensors and the sophisticated controllers found on every factory floor. PoE++ powers workstations and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). It gives you the freedom to design the physical layout: power lines do not have to be run, and HMIs can be installed in previously considered inaccessible areas. Also, with PoE++, you have the option of splitting its power so more devices can be run by a single industrial Ethernet switch.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is no longer an emerging technology; it is generating large-scale data in many industries. In fact, there were 8.74 billion connected IoT devices worldwide as of 2020, and another 1.33 billion will be added by the end of this year, with a forecast of 25.4 billion by 2030.² PoE++ is an exciting power solution for a large portion of these billions of devices. PoE++ can power small-scale devices more cheaply. For example, point of sale (POS) devices are becoming more sophisticated and need more bandwidth and higher power. In many businesses, iPads and other such devices are taking over POS duties, and the power usage is much greater than in the past. PoE++ can meet these demands by connecting multiple POS devices to a single PoE++ switch. And, of course, it also can supply enough juice for extremely power-hungry devices such as laptops and flat screens.
Digital Security
Security cameras are among the key devices that pushed PoE into the spotlight several years ago. The fact that PoE could provide power and communication for a camera over a single cable was genuinely revolutionary.
Now, with the higher power provided by PoE++, not just cameras can be powered but entire security systems: cameras, security controllers, ID scanners, and even door lock motors. It can do this by routing through a master control node at any point of entry, such as a smart doorbell.
Last Words
The benefits of PoE are many; it is flexible, safe, reliable, scalable, and it is quick to install and saves you money.
Versa Technology offers a broad range of PoE networking equipment, including switches, splitters, injectors, extenders, and hubs.
We can help you! Contact us today!
_______________________________________
Resources
1 SecurityInfoWatch.com: Harness the Latest PoE standard
2 Statista: Number of Internet of Things (IoT) Connected Devices Worldwide from 2019 to 2020
Further Reading Opportunities
5 Things You Need to Know About PoE Switches
7 Myths About Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Newly Emerging Levels of High Powered PoE