News about 5G seems to be everywhere these days. With all the noise surrounding this hip, new technology, it would be easy to dismiss all the hype as overkill. However, it is important not to overlook this latest generation connectivity standard’s unprecedented low latency, high speed, reliability, and flexibility. 5G is genuinely revolutionary and is positioned to provide numerous benefits for consumers and organizations alike.
What is 5G?
Qualcomm defines 5G as follows:
5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. It enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together, including machines, objects, and devices.
This wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users. Higher performance and improved efficiency empower new user experiences and connect new industries.
5G is based on several underlying technologies:
- OFDM: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing is “a method of modulating a digital signal across several different channels to reduce interference.”
- 5G NR: The “NR” stands for a ‘new radio’ interface and radio-access technology for cellular networks—a physical connection method for radio-based communication.”
Other examples of radio-access technologies include Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and 4G LTE.
- S-6 GHz and mmWave: 5G will operate in both lower bands, thus expanding its bandwidth enormously.
A Brief History of Mobile Networks
First Generation (1G)
1G was first introduced in Japan in 1979 and was rolled out in the US in 1980. This network was reliant on analog, which means it could only make phone calls; there was no texting. This network was notoriously unreliable and had security issues. Cell coverage dropped often, there was lots of interference from other radio signals, and the network could easily be hacked.
Second Generation (2G)
2G was introduced in 1991. It ran a digital signal (not analog) that significantly improved its capacity and security. With 2G, short message service (SMS) and multimedia messaging service (MMS) messages could be sent, although they were slow and often unsuccessful. In 1997, general packet radio service (GPRS) was launched, enabling users to send and receive emails.
Third Generation (3G)
3G hit the US in 2002 and wholly transformed mobile connectivity. Along with much greater speed, 3G users could use their phones for video calls, share files, surf the internet, watch online TV, and play online games. Suddenly, mobile phones became the hub of social connectivity. 3G is still in use today. However, all major cellphone carriers are planning to shut down 3G networks in 2022.
Fourth Generation (4G) 
Released in 2013, 4G is five times faster than 3G with speeds up to 100Mbps (at least theoretically). 4G offers connectivity for smartphones, tablets, and laptops and is noted for better latency, high-quality voice and streaming, fast downloads, and more.
Fifth Generation (5G)
According to multinational aerospace company, Thales Group:
The 5G network is on its way and is widely anticipated by the mobile industry. Many experts claim that the network will change not just how we use our mobiles but how we connect devices to the internet. The improved speed and capacity of the network will signal new IoT trends, such as connected cars, smart cities, and IoT in the home and office.
How is 5G better than 4G?
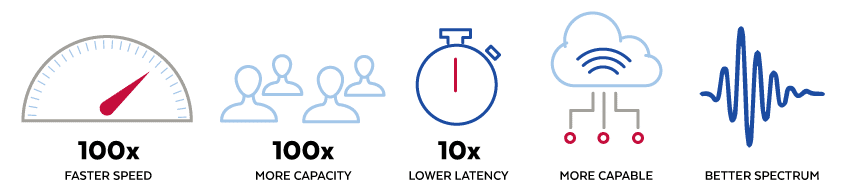
There are five significant ways that 5G is better than 4G:
- 5G is faster: It delivers up to 10 Gbps which is 100 times faster than 4G. So, for example, downloading a high-def film over a 5G network takes just nine minutes, while downloading the same movie over 4G will take 50 minutes.
- 5G has more capacity: It is designed to support 100 times more traffic than 4G.
- 5G has lower latency: It decreases end-to-end latency down to 1ms, which is ten times lower than 4G latency figures. As a result, 5G delivers significantly more instantaneous, real-time access.
- 5G is more capable: It is a more competent network that enhances the general mobile broadband experience and supports new services like mission-critical communications and the enormous Internet of Things. Per Qualcomm, “5G can also natively support all spectrum types (licensed, shared, unlicensed) and bands (low, mid, high), a wide range of deployment models (from traditional macro-cells to hotspots), and new ways to interconnect (such as device-to-device and multi-hop mesh).
- 5G makes better use of spectrum: Here is how Qualcomm explains it: “5G is also designed to get the most out of every bit of spectrum across a wide array of available spectrum regulatory paradigms and bands—from low bands below 1 GHz to mid bands from 1 GHz to 6 GHz to high bands known as millimeter wave (mmWave).”
Here is Why 5G is So Important
5G is driving remarkable global economic growth. Its impact is proving to be much greater than industry experts expected. Here are some statistics:
- The global 5G IoT market is on track to be $3.6 billion (USD) in 2021 and is projected to reach $11.2 billion (USD) by 2026.
- 5G’s total economic impact is expected to be realized by 2035, with a forecast of up to $13.1 trillion (USD) worth of goods and services globally.
- The “5G effect” could support up to 22.8 million jobs worldwide.
Last Thoughts
You may be asking yourself: Is 5G available now? The answer is yes. 5G started launching in 2019 and has been deployed in over 60 countries so far. Consumers have responded quite positively to this new technology, and the continuing 5G launch has good momentum.
Versa Technology aims to keep our customers fully informed about a broad array of communication and networking technology. We hope you found this article informative. Versa has over 25 years of experience in networking solutions. To learn more about our products and services, visit our homepage.